The Nifty 50 index is a critical benchmark within the National Stock Exchange (NSE), representing 50 carefully selected companies that provide insights into overall market conditions. As an investor, if you're looking to dive into this index, the first step is to open Demat account or open trading account with Bajaj Broking to facilitate your investments. The Nifty 50 serves as a reliable gauge of the Indian equity market, reflecting the performance of the largest publicly traded companies in India.

Understanding the Nifty 50 Index
The Nifty 50 index employs a capitalisation-weighted methodology, ensuring that the stocks within the index are weighted based on their free-float market capitalisation. This calculation method considers only the shares available for trading in the market, excluding those held by promoters or strategic investors. This design makes the index an accurate representation of the broader market.
The Nifty 50 encompasses various sectors, including Financial Services, Information Technology, Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) and Oil and Gas. This diversification provides investors with a balanced view of the market, showcasing both established industry giants and emerging powerhouses.
Nifty 50 Stocks: Weightage Breakdown
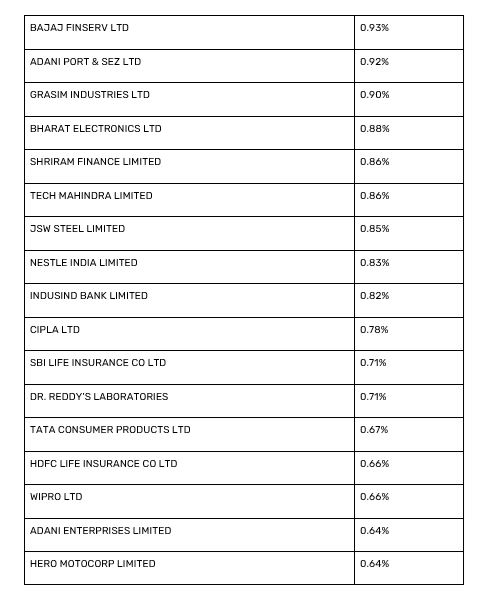
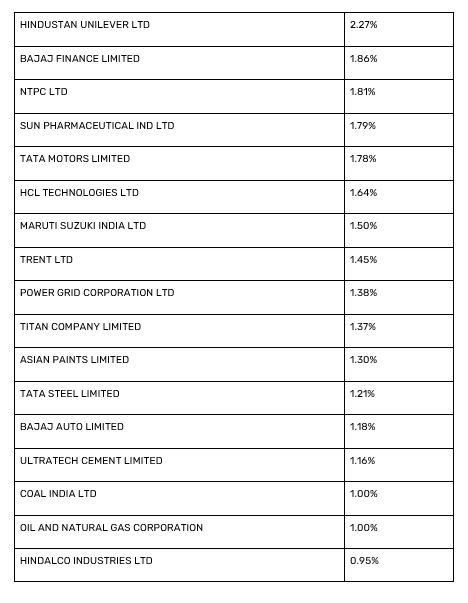
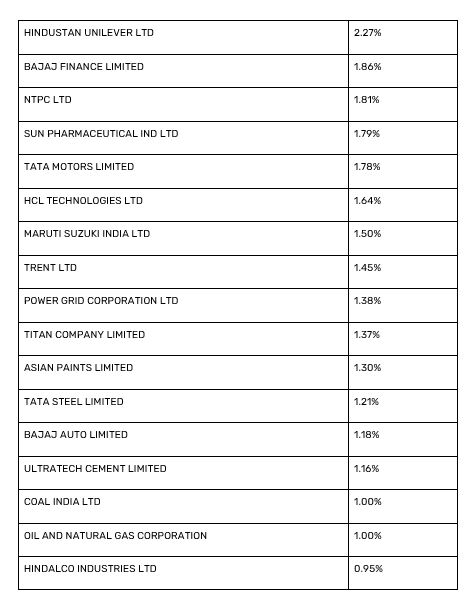
The following table lists the Nifty 50 stocks by their weightage in the index as of September 30, 2024. Understanding this weightage is essential for investors aiming to comprehend the index's composition and potential influence on market movements.

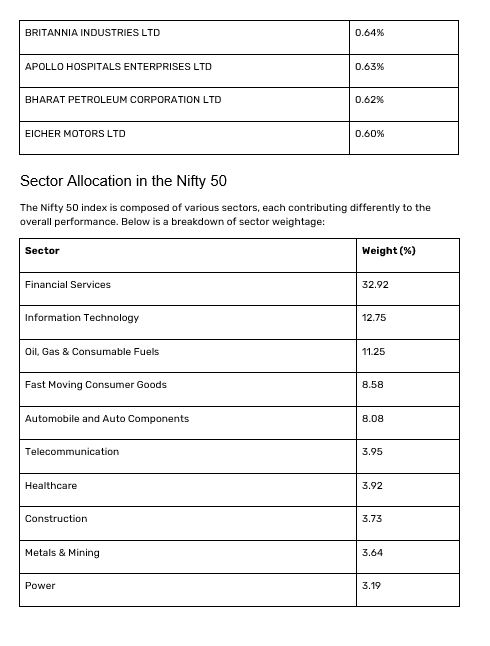
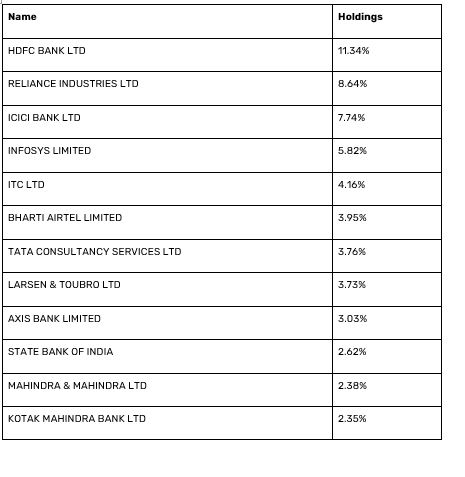
Understanding the sector allocation in the Nifty 50 allows investors to identify which segments are currently thriving and which may present future opportunities. For example, the Financial Services sector holds the highest weightage, suggesting its critical role in the Indian economy.
How is the Nifty 50 Index Computed?
The Nifty 50 index is computed using the free float market capitalisation-weighted method. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
1. Selection of Stocks: The NSE uses specific criteria such as liquidity, trading frequency and market capitalisation to select stocks for the index.
2. Free Float Market Capitalisation: This involves considering only the shares available for trading. The market capitalisation is calculated by multiplying the current market price of each stock by its free float.
3. Calculation of Index Value: The index value is computed using the formula:
Index Value = (Sum of (Market Capitalisation of Stock * Free Float Factor) / Base Market Capitalisation) * Base Index Value
4. Periodic Review: The Nifty 50 index undergoes periodic reviews to ensure that it reflects current market conditions. Stocks that no longer meet the eligibility criteria may be replaced by others that do.
Conclusion
The Nifty 50 index is an essential tool for investors, serving as a barometer of the Indian equity market. With its diverse sector allocation and carefully selected stock constituents, understanding the Nifty 50 provides valuable insights into market trends and investment opportunities. As you consider investing in this index, ensure you take the necessary steps to open Demat account with Bajaj Broking to facilitate your journey in the stock market.